
A Detailed Understanding Of Takt Time, Cycle Time, And Lead Time
Table of Contents
With the forthcoming industrial uprising, digitization, and IIoT technology underway, multiple resources seem to simplify technology adoption. Many people are still unsure regarding concepts like cycle times, lead times, and takt times in the interim. A company’s potential to survive and expand within a particular industry can be greatly impacted by its ability to monitor and manage production metrics. This can be the distinction between a company succeeding in the competitive landscape and falling out of business.
Takt time, cycle time, and lead time represent a few of the most often tracked metrics throughout plenty of discrete industry resources, while there are also many more KPIs to monitor.
What Is Takt Time?
Takt time refers to the pace at which a product or service needs to be finished in order to meet demand from customers. By synchronizing the rate of production with customer demand, organizations can increase overall productivity, prevent excessive production, and save inventory expenses. Put another way, a takt time is the rate of production and is essentially the lifeblood of the workflow. With it, businesses can maximize their ability to fulfill demand without creating too much or too little.
How To Measure Takt Time?
There’s significantly more to the takt time computation than just a time-demand formula. It is the ideal starting point for considering various approaches to the analysis of production time and the most effective ways to plan and use that time to satisfy demand, from the viewpoints of customers and manufacturers alike.
Takt Time = Net Production Time/Customer Demand (formula convert it into image)
Benefits Of Calculating Takt Time
- Calculating the duration of any service delivery procedure
- Maintaining a steady and efficient flow of production
- There will be fewer mistakes made by the company, and the total quality will rise.
- Reducing the amount of overtime that employees work
- Minimizing training times to increase productivity
How To Reduce Takt Time In Business?
Takt time can only be decreased by process optimization since it is the rate at which production must operate to fulfill demand. Efforts for constant enhancement can help Takt time to match demand; as operations get better, each product’s cycle time gets closer to the needed speed. By boosting output effectiveness through enhanced operations planning and methods, takt time can be significantly reduced. Production is accelerated as a result, closing the discrepancy between supply and demand.
Businesses can plan resources for instances where the takt time might be higher or lower than anticipated by assessing the cycle times and comprehending their degree of complexity. They can better balance out takt time by using this metric to guide their planning and time management decisions. The subsequent step in measuring and optimizing cycle and takt times is figuring out where the production operation is causing variability, delays, and inefficiencies. These are the inefficiencies and blockages that keep businesses from reaching their desired turnaround time.
What Is Cycle Time?
Cycle time is the duration of time needed to finish a single work cycle. This can apply to software creation cycles, customer support processes, manufacturing procedures, etc. Cycle times are important for process optimization since they show the speed at which a process moves along and help determine when adjustments should be made. Cycle times can be shortened to promote overall effectiveness and prevent expensive errors. Businesses can find issues with the flow of their processes and come up with plans for boosting productivity by analyzing cycle time.
How To Measure Cycle Time?
To get an accurate measure of cycle time, businesses must first determine the total amount of time involved in completing one cycle. This could include all preparation and setup activities, any waiting periods for equipment or materials, as well as execution and review times. Once the total amount of time has been determined, divide that number by the number of cycles completed over the same period.
Cycle Time = (Total Time/Number of Cycles) (formula convert it into image)
Benefits Of Calculating Cycle Time
- Determines areas that require enhancement
- Increases promptness and accuracy
- Enhanced flexibility and agility
- Timely verification and risk reduction
- Allocating resources effectively
How To Reduce Cycle Time In Business?
Businesses can gain a competitive edge by cutting cycle times in two ways. First, by delivering completed products more quickly, businesses can cut lead times by reducing cycle times. Second, shorter cycle times enable businesses to shorten lead times and develop new products more quickly. The method of production of a part or final product is explicitly plotted on a process map at each workstation as well as throughout the process. Teams can find and execute enhancements with the help of process mapping.
Knowing the variations between cycle time and lead time as well as how they function together is crucial. Businesses are going to have a longer time within their normal lead time if they can shorten their cycle time. This allows them to reorganize their procedures in a way that is more beneficial to the business. Reduced cycle times can open up chances for extra enhancements that were not achievable when they had to rush everything. Now since businesses are able to provide a faster delivery guarantee, they can take on more orders, charge more to expedite particular items, or cut their lead time.
What Is Lead Time?
The lead time is the time frame of any particular process from the beginning to the end. Reducing lead time can improve efficiency and optimize operations by raising production and income. Extended lead times, however, have a detrimental effect on output and revenue. Consequently, the shortest lead times are associated with the most effective manufacturing schedules. Lead times are crucial to the company’s profitability; even a minor improvement can have a big effect on sales, whereas a tiny drop can have a major adverse effect.
How To Measure Lead Time?
The lead time calculation equation would vary substantially depending on the industry. However, the underlying concept is to incorporate all the different places where time is consumed during the operation. Businesses would thus need to take into consideration all of these different factors. Generally speaking, the lead time calculation might resemble the following:
Lead Time = Pre-processing Time + Processing time + Waiting time + Transportation time + Storage time + Inspection time (formula convert it into image)
Benefits Of Calculating Lead Time
- Decreased likelihood of overstocking and preventing losses
- Calculate the production’s efficacy.
- Improved planning and estimation
- Enhanced contentment among clients
- Broadened management of the distribution network
How To Reduce Lead Time In Business?
Any company can be made more efficient by being capable of providing products and services on time. Often, this only requires a few small adjustments that add up to big gains. Above all, businesses could conserve money by reducing lead time. The mapping of values should be employed by the business to pinpoint non-value-added tasks that increase lead times. Make a checklist of these tasks, cross out the ones the business can operate without, and keep the ones that improve the standard of production.
Businesses implement the practice of vertical integration as a tactic for covering up wasted time in product delivery. It enables a business to manufacture its other parts and raw materials, reducing lead times and overhead expenses. A simple way for manufacturers to cut lead times is to prioritize working with manufacturers who are local to the factory or warehouse. Additionally, think about making bigger (but less regular) orders from foreign vendors and maintaining a larger stockpile on hand if the business is unable to track down a local source that can match their offer on pricing.
Cycle Time Vs Lead Time: What Is The Difference?
In short, lead time is the amount of time that passes between receiving an order from a customer and having it fulfilled, whereas cycle time is the amount of time that a team needs to manufacture a product. Since cycle time falls within the lead time timeline, lead time will always be greater than cycle time.
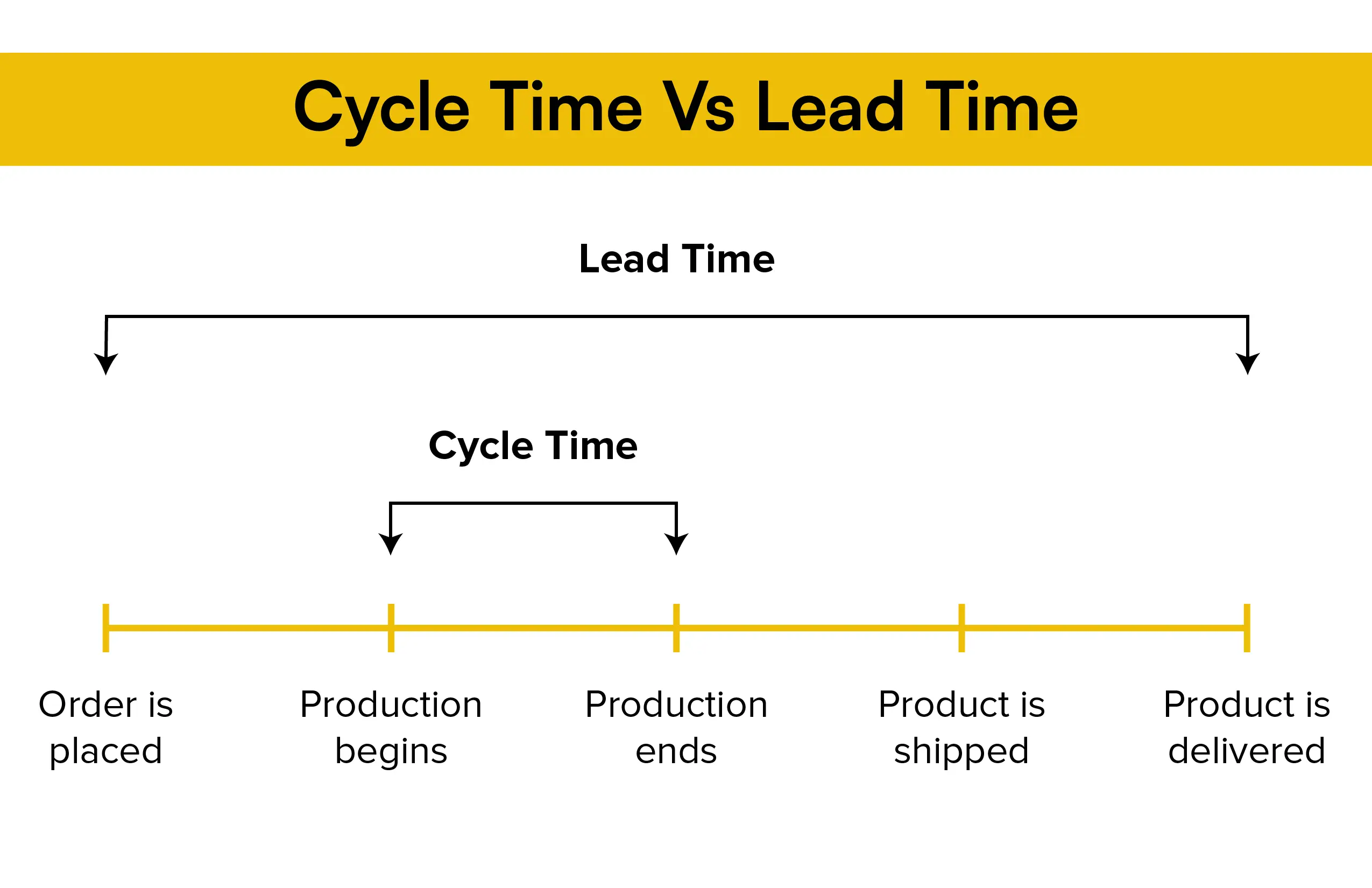
In every case, it is beneficial for the company to monitor both lead time and cycle time as, in addition to their relationship, an understanding of the cycle time for a product’s manufacturing plays a significant role in estimating lead time. One strategy to shorten lead times is to manage the cycle time, which can give businesses a competitive edge.
Conclusion
In align=”justify”business, the words Takt Time, Cycle Time, and Lead Time are sometimes used similarly. The terminology and methods of calculation of each of these measurements, however, clearly diverge from one another. It is possible to optimize processes’ workflow, supplies, and work hours by knowing the way each one of these is utilized.
Agile business uses Cycle Time, Lead Time, and Takt Time as metrics to assess product reliability and effectiveness while cutting down on pointless interruptions and procedures. To remain at the forefront of developments, a business’s capacity to manage production will depend on the manner in which these times are acquired and utilized.